
Learn about Cannabinoids

Cannabinoids
CBD
THC
CBN
CBG
THCV
CBC
THCA
CBDA
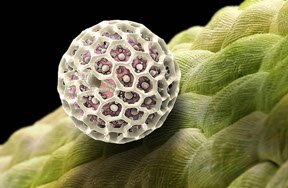
Cannabinoids are a class of diverse chemical compounds that activate cannabinoid receptors on cells that repress neurotransmitter release in the brain. These receptor proteins include the endocannabinoids (produced naturally in the body by humans and animals), the phytocannabinoids (found in cannabis and some other plants), and synthetic cannabinoids (produced chemically by humans). The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound of cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is another major constituent of the plant, representing up to 40% in its extracts. There are at least 100 different cannabinoids isolated from cannabis, exhibiting varied effects.
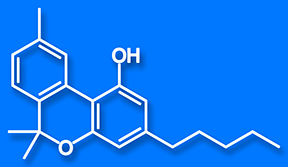 CBD/Cannabidiol
CBD/Cannabidiol
• Cannabidiol or CBD, is a non-psychoactive component in cannabis that has medical effects but does not make the patient feel stoned.
• CBD reduces the effects of THC.
• CBD, is the 2nd most frequently found compound in cannabis.
• CBD, is one of cannabis's most medicinal cannabinoids.
• Because Medical Cannabis remains in its infancy, case studies regarding CBD are just beginning to emerge.
• Because CBD is non-psychoactive, (Does does get one high) it can be used in larger and more concentrated doses.
• Because it is non-psychoactive, CBD a good choice in the treatment of animals
• CBD is know to help shrink tumors, reduce anxiety and regulate appetite.
• CBD can dramatically reduce the symtoms of epilepsy, autism, crohn's desease, as well as a host of other ailments.
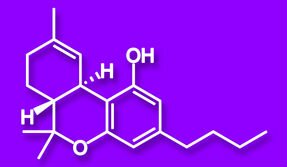
THC/Tetrahydrocannabinol
THC is the most abundant and widely known cannabinoid in cannabis. THC is the cannabinoid responsible for the main psychoactive effects patients are familiar with. The compound is a mild analgesic and cellular research has shown the compound has antioxidant activity. THC is believed to interact with parts of the brain normally controlled by the endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter anandamide.
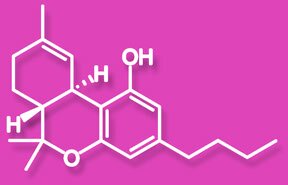
CBN/Cannabinol
A psychoactive cannabinoid that comes about from the degradation of THC, there is usually very little CBN in a fresh plant. CBN potentiates the effects of THC. The degradation of THC, into CBN, is often described as creating a "couch lock" effect.
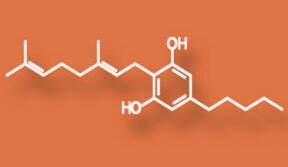
Cannabigerol/CBG
A nonpsychoactive cannabinoid, CBG has antibacterial effects and can alter the overall effects of Cannabis.
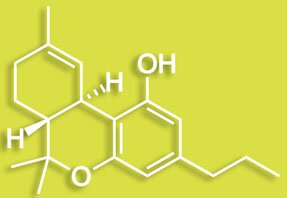
Tetrahydrocannabivarin/THCV
THCV is found in largest quantities in Cannabis sativa strains. It is currently being developed as a treatment for metabollic disorders including diabetes. THCV has been shown to block the psychoactive effects of THC.
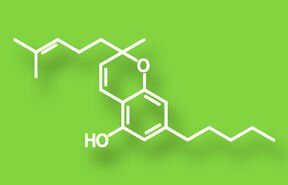
Cannabichromene/CBC
More common in tropical cannabis varieties. Effects include anti-inflamatory and analgesic.
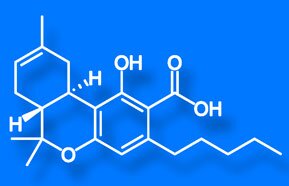
THCA is the main constituent in raw cannabis. THCA converts to D9-THC when burned, vaporized, or heated for a period of time at a certain temperature. THCA holds much of the anti-inflammatory properties, as well as anti-proliferative (inhibiting the cell-growth in tumors/ cancer cells,) as well as anti-spasmodic (suppresses muscle-spasms.)
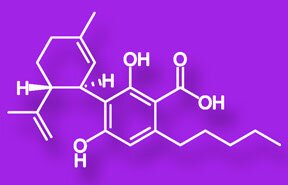
CBDA, similar to THCA, is the main constituent in cannabis that has elevated CBD levels. THCA and CBDA hold most of the anti-inflammatory properties that cannabis has to offer.



